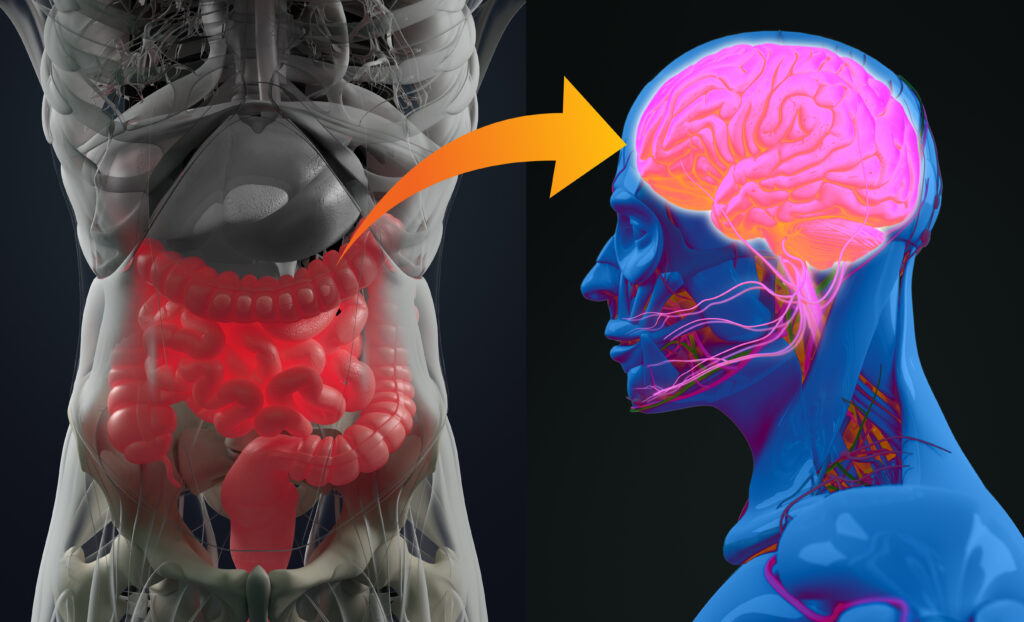
Over the last decade, the human gastrointestinal microbiome and its role in health and disease has risen as a research hotspot. In addition to its undeniable connection to the brain and immunity, emerging studies have uncovered the link between gut health and skin health, aptly referred to as the gut-skin axis. Researchers have found that gut dysbiosis, or an imbalance of microorganisms in the intestines, not only alters the skin microbiome, but may also contribute to a variety of skin disorders and diseases.1 This includes acne, psoriasis, rosacea, and atopic dermatitis. To provide patient education on ways to improve skin health through the gut, it’s important for healthcare professionals to understand the role of the skin microbiome, how it is affected by the gut and science-based recommendations that could be beneficial for both areas of the body.
Uncovering the Skin Microbiome
The term “gut-health” has skyrocketed in popularity because of improved scientific understanding of the relationship between digestive health to overall well-being, and an increase in rates of digestive diseases, such as IBS, worldwide.2 While most are familiar with the microbiome in regard to the intestine, the skin microbiome has become an emerging area of research, especially in its relationship to gut health and the immune system. Aside from being the body’s largest organ, the skin is host to millions of microorganisms, including bacteria, fungi, and viruses, that play a similar role to those found in the gut. This includes fending off disease-causing pathogens and aiding immune defenses. As with the gut, maintaining a balanced skin microbiome involves a complex interplay among microorganisms, immune cells, and other factors. Alteration of the skin microbiome, specifically an increase in pathogenic microorganisms and a decrease in beneficial ones, can cause inflammation and changes in the immune system. As a result, conditions such as acne and eczema may occur.3
Gut-Skin Axis: A Look at the Latest Research
The gut-skin axis is a term used for the intricate interaction between the gut and the skin and essentially acts as a two-way street – meaning intestinal health or conditions can impact the skin and vice versa. The gut and skin are uniquely related in purpose and function, especially with both being essential to the maintenance of physiological homeostasis. The integrity of the intestinal barrier, along with the action of intestinal mucus, immune cells, and other factors, prevents the entrance of bacteria into the bloodstream, ultimately maintaining skin homeostasis.4 When intestinal integrity is disrupted, the imbalance of microbes that ensues can ultimately lead to a state of skin disease.5 Considering the varied types of gut symptoms, the skin may be a good measure for determining what may be happening in the gut. Not to mention that the health of the skin barrier, or the outermost later of the skin, plays a direct role in gut health as it protects against bacteria, toxins and other harmful substances which may lead to inflammation which can negatively affect gut health.
While the mechanisms of which the gut microbiome affects skin health are still unclear, advancements toward understanding the skin and gut microbiome may lead to novel ways to treat human skin diseases.
Role of Diet & Probiotics
Ongoing research suggests probiotics have an impact on the composition and metabolic activities of the gut microbiome, which subsequently impacts the skin. Modifying the gut microbiome through dietary changes and ingestion of certain macro- and micro-nutrients significantly influence the composition and diversity of the gut microbiome which could positively impact skin health and prevent related diseases. For example, dietary fiber can help to increase beneficial bacteria, and some micronutrients such as vitamins A, D, and calcium, help to modulate gut microbiota toward a health phenotype by also increase beneficia; bacteria strains, all of which can positively affect skin health.6
Furthermore, using dietary supplements that include probiotics and prebiotics may help reshape the composition of our gut microbiome in the long term. The most common bacteria strains in probiotics supplements includes Bifidobacterium, Lactobacillus, and Streptococcus with Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus being the two most used strains in human health studies.6 However, the use of probiotics and prebiotics in topical treatments for conditions such as acne and atopic dermatitis remains to be an area of ongoing research and controversy.4
Putting Action into Practice
As interest in digestive health takes center stage, and science behind its relationship to skin health continues to surface, healthcare professionals are well-positioned to educate patients on ways to improve their health through food and nutrition. Here are 3 simple tips to improve gut health, and ultimately, skin health, from gastrointestinal expert dietitian and member of Orgain’s Nutrition Advisory Board, Colleen Webb, MS, RD.
Choose probiotics wisely. Probiotic supplements may help to manage digestive symptoms. Emerging research suggests probiotics might also benefit skin health by improving barrier function, reducing inflammation, balancing its microbiome, and moisturizing. However, not all probiotics are created equal, and different strains have varying effects. Recommendations for probiotics should be based on those that have been well-studied and have shown a benefit to the individual concerns or medical conditions. Gastrointestinal healthcare experts can support in making these recommendations.
Consider a vitamin D supplement. Vitamin D supports the integrity and function of both the gut and skin barriers. Low vitamin D levels have been linked to increased risk of a variety of diseases, including the onset and reactivation of inflammatory bowel disease and psoriasis. A sufficient vitamin D level (measured as 25-hydroxy vitamin D) is considered >30 ng/mL, but many experts aim for >40 ng/mL. Since it can be difficult to adequately meet vitamin D needs with diet alone (e.g. tuna, vitamin D fortified cereals, orange juice and dairy/non-dairy alternatives) a supplement may be recommended. The supplemental dose is typically 500-5,000 IU to correct any deficiencies, with a maintenance dose of 1,000-2,000 IU/day. While vitamin D can also be synthesized from the sun, the amount produced can vary from person to person, not to mention too much sun exposure can damage skin cells.
Increase fiber intake. Eat a wide variety of plants, such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables. They provide an ample amount of dietary fiber, which aids digestion and promotes regular bowel movements. Good digestion (plus hydration!) eliminates toxins, which is essential for healthy skin. Plus, fiber supports a healthy microbiota, which affects gut and skin health via regulating the immune system. Aiming for 30 unique plants per week is an excellent way to eat more plants.
Eat whole or minimally processed foods. Eat a diet rich in plants, such as fruits and vegetables; healthy fats, like olive oil, avocado and fatty fish; and lean protein sources, including poultry and eggs. This type of dietary pattern (e.g. the Mediterranean diet) is full of antioxidants and anti-inflammatory agents that nourish both gut and skin health.
Stay hydrated. Water is essential for healthy skin and digestion for a variety of reasons. The most noticeable benefits include its ability to protect against dry skin and help to alleviate constipation. Some people can let thirst guide their fluid intake, whereas others need to actively drink water. A good rule of thumb is to divide current body weight in pounds by two and drink that many ounces of fluid per day. For example, a 150-pound individual would need approximately 75 ounces of water per day or 9 cups.
Also, while its benefits for skin health are better understood, some research suggests collagen peptides may support gut health, as well.7
In providing recommendations to your patients or clients of foods that support the health of both the gut and skin, Orgain provides a wide array of options including:
- Orgain Grass-Fed Pasture-Raised Collagen Peptides
- Orgain’s grass-fed, pasture-raised collagen peptides powder mixes easily into any hot or cold liquid and supports hair, skin, nails, and joint health.* In addition, it’s:
- Packed with 20 grams of collagen peptides per 2-scoop serving
- Made with Type I & III grass-fed & pasture-raised collagen peptides
- Non-GMO, gluten free, no added sugar
- Made without soy, dairy, lactose
- Contains no artificial flavors, sweeteners, or preservatives
- Orgain’s grass-fed, pasture-raised collagen peptides powder mixes easily into any hot or cold liquid and supports hair, skin, nails, and joint health.* In addition, it’s:
- Orgain Grass-Fed & Pasture-Raised Collagen + Probiotics – exclusively at Costco
- From skin and joint health to gut health, Orgain’s Collagen + Probiotics is a powder that is flavorless, odorless and easily dissolves in hot or cold liquids. Here are a few other nutritional highlights:
- Contains Type I & III grass-fed & pasture-raised collagen peptides
- Includes prebiotics and 1 billion probiotics from 5 strains:
- Bacillus Coagulans
- Lactobacillus Plantarum
- Bifidobacterium Longum
- Bifidobacterium Breve
- Pediococcus Acidilactici
- Non-GMO, gluten-free, no added sugar
- Made without soy, dairy, lactose
- No artificial flavors, sweeteners, or preservatives
- From skin and joint health to gut health, Orgain’s Collagen + Probiotics is a powder that is flavorless, odorless and easily dissolves in hot or cold liquids. Here are a few other nutritional highlights:
- Orgain Hydro Boost Rapid Hydration Drink Mix – provides effective hydration using food-based, high-quality, organic ingredients, and is made to meet the World Health Organization’s guidance on fast rehydration. Here are some additional highlights of Orgain Hydro Boost:
- Contains 5x electrolytes with 50% less sugar compared to traditional sports drinks
- Enhanced with superfoods.
- Balances key electrolytes and ingredients including pink Himalayan salt and organic cane sugar to replenish fluids and restore hydration. This combination of sodium, glucose and citrate improves the delivery of electrolytes and fluids into cells faster than water alone to provide everyday wellness hydration.
- Orgain Superfoods + Probiotics
- Includes 1 billion probiotics (Bacillus Coagulans) per 1-scoop serving
- Includes 50 organic superfoods
- Non-GMO, gluten-free, no added sugar
- Made without soy, dairy, lactose
- No artificial flavors, sweeteners, or preservatives
Learn More with Orgain
Looking to further your knowledge on the impact of nutrition for skin health? Check out this podcast episode and science-based brief:
The Good Clean Nutrition Podcast
Episode 14: Exploring the Benefits of Dietary Collagen for Skin, Joints & Overall Health with Molly Kimball, RD, CSSD
Science-Based Brief
Exploring the Evidence on Nutrients in Skin Health – June 2022
- De Pessemier, B., Grine, L., & Debaere, M., et al., (2021, February 11). Gut-skin axis: Current knowledge of the Interrelationship between microbial dysbiosis and skin conditions. Microorganisms. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7916842/
- Wang, R., Li, Z., & Liu, S. (2023, March 28). Global, regional, and national burden of 10 digestive diseases in 204 countries and territories from 1990 to 2019. Frontiers in public health. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10088561/
- Criswell, L. A. (2022, March 21). Unraveling the role of the skin microbiome in health and disease. National Institutes of Health. https://directorsblog.nih.gov/2022/03/22/unraveling-the-role-of-the-skin-microbiome-in-health-and-disease/
- Lee, H.-J., & Kim, M. (2022). Skin barrier function and the microbiome. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(21), 13071. . https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232113071
- Mahmud, Md. R., Akter, S., Tamanna, S. K., et al., (2022). Impact of gut microbiome on skin health: Gut-skin axis observed through the lenses of Therapeutics and skin diseases. Gut Microbes, 14(1). https://doi.org/10.1080/19490976.2022.2096995
- Yang, Q., Liang, Q., Balakrishnan, B., et al., (2020). Role of dietary nutrients in the modulation of gut microbiota: A narrative review. Nutrients, 12(2), 381. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12020381
- Abrahams, M., O’Grady, R., & Prawitt, J. (2022). Effect of a daily collagen peptide supplement on digestive symptoms in healthy women: 2-phase mixed methods study. JMIR Formative Research, 6(5). https://doi.org/10.2196/36339
Episode 27: Understanding & Optimizing the Mind-Gut-Immune Connection with Dr. Emeran Mayer
In this episode of The Good Clean Nutrition Podcast, host Mary Purdy, MS, RDN, speaks with Dr. Emeran Mayer, one of the foremost experts on the gut-brain-immune connection, to discuss how to harness the power of the mind-gut connection to take charge of our health. Tune in as they breakdown how the mind-gut connection affects mental health, immune function, along with diet & lifestyle changes to help balance the gut to improve full-body health.
Be sure to subscribe to The Good Clean Nutrition Podcast on your favorite podcast platform and listen to more episodes at https://healthcare.orgain.com/podcast.
Ambassador Spotlight: Dr. Neal Patel

What is your current title? If you have a unique niche, share more about why you’ve made this your focus.
Physician/ Co-Founder: Indy Wound Center for Limb Preservation & Reconstruction
Role: Wound Care & Reconstructive Surgeon
I’m a physician specializing in wound care and surgical restoration of hard to heal wounds. Wound care is often overlooked and passed over by many physicians leading to amputation and sometimes death of patients, that could otherwise have been prevented if they were able to see a dedicated wound care provider. I’m in the business of providing patients with a better quality of life and giving them other options of healing.
Tell us about your professional journey and any obstacles you’ve had to overcome.
I grew up in a small town in Indiana where health was not a priority. People had to focus on work and providing for their families. This often led to high incidences of diabetes. With the combination of demanding physical jobs and diabetes, some people developed ulcerations, which often led to amputations due to the lack of resources and physicians trained in limb salvage. I eventually went onto undergrad at Indiana University, medical school in Ohio, and then trained at a Veterans Affairs Medical Center in Chicago. This is where I witnessed firsthand the importance of limb preservation in our veteran population. My training involved surgical and non-surgical management of various lower extremity conditions with an emphasis on wound care, amputation prevention, deformity correction, and infection management.
Upon completion of this residency, I relocated to Southern California and completed a fellowship in advanced wound care, diabetic limb salvage and lower extremity reconstructive surgery. During my time in Los Angeles, I maintained privileges at Cedars Sinai Medical Center and worked alongside leaders in the fields of plastic, vascular, and orthopaedic surgery. After a couple years in Los Angeles, I made the decision to go back home and help the people that led me to this career. I co-founded Indy Wound Center for Limb Preservation & Reconstruction, where we focus strictly on full body wound care and restoration.
Why do you recommend Orgain?
Being a wound care specialist requires looking at a patient as a whole and figuring out the true etiology and systemic factors as to why a wound is not healing. And an important part of this process, if not the most important, is nutrition. I recommend Orgain organic nutrition shakes, protein shakes/powders and collagen powders to all my patients and have seen huge success in wound healing with the supplementation of these products. Patients love the taste and feel that they are a tangible part of the process of healing.
##
2023 Orgain Ambassador Surveys – The Results are In!
Huge thank you to all ambassadors that participated in our two recent surveys to assess ambassador program satisfaction and recommendations of Orgain products. Please know that this feedback is instrumental in helping to shape our educational programs to better suit the needs of healthcare professionals.
We’re proud to share that 90% of ambassadors are preferentially recommending Orgain versus other oral nutrition supplements. Below, we’ve shared some other ratings based on a 5-star scale for the educational resources and programs we offer. Feel free to click on each link to learn more:
- Orgain Healthcare Ambassador Program – 4.8/5
- Professional Educations Series – 4.6/5
- The Good Clean Nutrition Podcast – 4.3/5
- The Ambassador Sampling Portal – 4.8/5
Thank you again for participating in this survey and stay tuned for more new educational resources and ambassador sampling portal updates to better support you in practice! Do you have any other questions or suggestions for the Orgain Healthcare Team? Share a post here in the Orgain Healthcare Ambassador Collective private Facebook Group!
With the rising interest in collagen as a supplement solution that offers multiple, complimentary benefits, Orgain has established itself as a trusted leader in high-quality collagen products and education. See below for nutritional highlights on two of our most popular collagen products.
Orgain Grass-Fed & Pasture-Raised Collagen Peptides

Orgain’s grass-fed, pasture-raised collagen peptides powder mixes easily into any hot or cold liquid and supports hair, skin, nails, and joint health.* In addition, it’s:
- Packed with 20 grams of collagen peptides per 2-scoop serving
- Non-GMO, gluten free, no added sugar
- Made without soy, dairy, lactose
- Contains no artificial flavors, sweeteners, or preservatives
- Made with Type I & III grass-fed & pasture-raised collagen peptides
Orgain Grass-Fed & Pasture-Raised Collagen + Probiotics – exclusively at Costco

From skin and joint health to gut health, Orgain’s Collagen + Probiotics is a powder that is flavorless, odorless and easily dissolves in hot or cold liquids. Here are a few other nutritional highlights:
- Non-GMO, gluten-free, no added sugar
- Made without soy, dairy, lactose
- No artificial flavors, sweeteners, or preservatives
- Contains Type I & III grass-fed & pasture-raised collagen peptides
- Includes prebiotics and 1 billion probiotics from 5 strains:
- Bacillus Coagulans
- Lactobacillus Plantarum
- Bifidobacterium Longum
- Bifidobacterium Breve
- Pediococcus Acidilactici
To learn more about collagen and its many functions that stem beyond the commonly known benefits for skin, hair and nails, check out and share our latest educational resource, An Overview on Collagen, which includes excellent science-based information to share with your patients or clients. You’ll also learn more about the type of collagen used in Orgain Collagen Peptides.
*These statements have not been approved by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
July 13, 2pm EST: Skin Health and Nutrition: Separating the Science from the Trends, presented by Nancy Collins, PhD, RDN, LD, NWCC, FAND > Register now

August 10, 2pm EST: Foods That Activate Your Gut, Brain, and Metabolism, presented by William W. Li, MD > Register now

August 24, 2pm EST: Nutrition Considerations for the Youth Athlete, presented by Laura M. Reece, MS, RD, CSSD, LDN > Register now
Did you know that the Orgain Healthcare Professional Education Webinar Series can be easily accessed on the Orgain Healthcare App? Whether on-demand or live, all the webinars in this series are available for 1.0 CPEU for RDNs and NDTRs. Learn More.



